Light Emitting Diode (LED)
Description
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when an electrical current passes through it. LEDs are known for their energy efficiency, small size, and long operational lifetime.
Characteristics
- Efficiency: LEDs are highly efficient and convert a greater proportion of energy into visible light rather than heat.
- Durability: They are robust and resistant to shock, vibration, and temperature changes.
- Longevity: LEDs have an extended lifespan, often lasting for tens of thousands of hours.
- Brightness: They offer high brightness with low power consumption.
- Size: LEDs are available in various sizes, allowing for compact designs.
- Color: LEDs come in a wide range of colors, including infrared and ultraviolet, with the ability to create white light.
Identification Methods
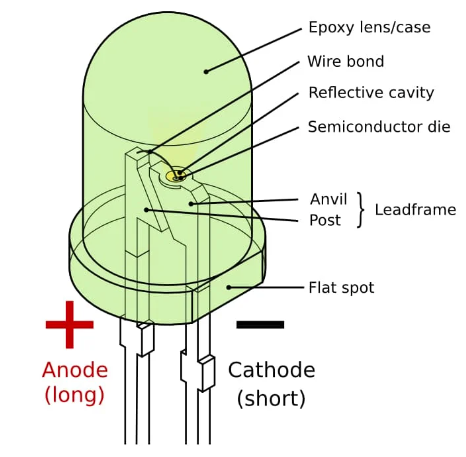
- Visual Inspection: LEDs have a characteristic flat or hemispherical lens shape.
- Polarity: Identify the anode (longer lead) and cathode (shorter lead) using a multimeter or by observing the flat side on the lens, which indicates the cathode.
- Color Coding: The color of the LED can be an indicator of its peak emission wavelength.
Common Applications
- General Lighting: In residential, commercial, and public spaces for energy-efficient lighting.
- Automotive: For brake lights, turn signals, and interior lighting in vehicles.
- Electronics: As indicator lights in various electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and smartphones.
- Horticulture: In grow lights for plants, providing specific light spectra for plant growth.
- Signage and Displays: For billboards, advertising displays, and digital signage.
- Medical Devices: In various diagnostic and therapeutic equipment.
- Astronomy: As light sources for telescopes and observational equipment.
Usage Tips
- Ensure correct polarity when connecting LEDs to avoid damage.
- Use appropriate resistors to limit current and prevent overheating.
- Consider heat dissipation mechanisms for high-power LEDs to maintain efficiency and longevity.
Examples
- Proejct 1 Blinking LED (on Arduino)